Help
Where to start?
- Page tour
 The home page, search page and SNP page include the 'page tours' in the bottom right corner. Use this icon!
The home page, search page and SNP page include the 'page tours' in the bottom right corner. Use this icon!
What is ASB?
ASB stands for Allele-Specific Binding. A Transcription Factor (TF) might prefer to bind one of two alternative alleles of homologous chromosomes and thus exhibit allele-specific binding. ASB highlights regulatory SNPs with high potential to affect gene expression. Systematic dissection of ChIP-Seq data processed in the GTRD database allowed us to identify hundreds of thousands ASB events for a wide range of transcription factors. 

Glossary
- Coordinate system
- Genome positions of ASBs and SNVs in the database are vcf/gtf-like (1-based), hg38 genome assembly.
- BAD
- Background Allelic Dosage (BAD) is the expected ratio of major to minor allelic frequencies in a particular genomic region.
For example, if a copy number of two alternating alleles is the same (e.g. 1:1 (diploid), 2:2, or 3:3), then the respective region has BAD=1, i.e. the expected ratio of reads mapped to alternative alleles on heterozygous SNVs is 1. All triploid regions have BAD=2 and the expected allelic read ratio is either 2 or ½. In general, if BAD of a particular region is known, then the expected frequencies of allelic reads are 1/(BAD +1) and BAD/(BAD + 1). Whole genome BADmaps are obtained with BABACHI. More details can be found in the ADASTRA paper. - ADASTRA coverage filters
- ADASTRA pipeline utilizes several SNV filters before statistical evaluations of ASB:
- Heterozygous biallelic SNVs (according to GATK ‘GT’ annotation);
- Having ≥ 5 reads at each of the alleles;
- Present in dbSNP build151 ‘common’ collection;
- Belonging to the regions with BABACHI-estimated BAD;
- Having a total read coverage of ≥ 20 in at least one of the experiments (for a particular TF or cell type).
ASB properties
- ASB significance
- ASB significance ASB calling is done separately for each ChIP-Seq experiment. For each candidate ASB site, the P-values for Reference and Alternative allele are calculated separately according to the fitted Negative Binomial Mixture model accounting for different assignment of the alleles to the higher or lower DNA copies in genomic regions with BAD > 1. Prior mixture weights obtained with the global fit across SNVs were updated with Bayesian estimation separately for each SNV.
For a particular SNV, the P-values from individual data sets are aggregated with the logit (Mudholkar-George) method for each TF (using ChIP-Seq data from all cell types) and cell type (using ChIP-Seq data from all TFs) and FDR-corrected with the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure for SNVs (for each TF and each cell type separately). - ASB effect size
- The Effect Size of an ASB event is calculated separately for Reference and Alternative alleles and is defined as the weighted mean of log-ratios of observed and expected allelic read counts, with weights being -log10 of the respective P-values. The expected read counts are estimated from the fitted Negative Binomial Mixture model accounting for different assignments of the allies to the higher or lower DNA copies in genomic regions with BAD > 1. Prior mixture weights obtained with the global fit across SNVs were updated with Bayesian estimation separately for each SNV.
The Effect Size is not assigned (n/a) if all of the raw individual P-values of an SNV on a particular genome position are equal to 1, considering Ref- and Alt-ASBs separately.
Motif annotation
- Motif P-value
- For transcription factors with motifs available in the HOCOMOCO v.11 core collection, the P-values of the best hits were calculated for Reference and Alternative allelic variants using SPRY-SARUS. The motif position was fixed according to the best hit considering both the Reference and the Alternative alleles on both DNA strands.
- Motif Fold Change
- Motif Fold Change is the log2-ratio between Reference and Alternative Motif P-values. Positive values indicate Alt-ASBs (preferred binding to the Alternative allele). Negative values indicate Ref-ASBs. The value is not assigned (n/a) in case the sequence motif model was not available.
- Motif Concordance
- Motif Concordance indicates whether the allelic read imbalance is consistent with the transcription factor motif Fold Change (FC, predicted from sequence analysis). The following notation is used:
- n/a: Motif is not available;
- No hit: The best hit P-value is higher than 0.0005 threshold;
- Weak concordant: The absolute value of FC is less than 2 but consistent with the allelic read imbalance;
- Weak discordant: The absolute value of FC is less than 2 and not consistent with the allelic read imbalance;
- Concordant: The absolute value of FC is greater or equal to 2 and consistent with allelic read imbalance;
- Discordant: The absolute value of FC is greater or equal to 2 but not consistent with allelic read imbalance.
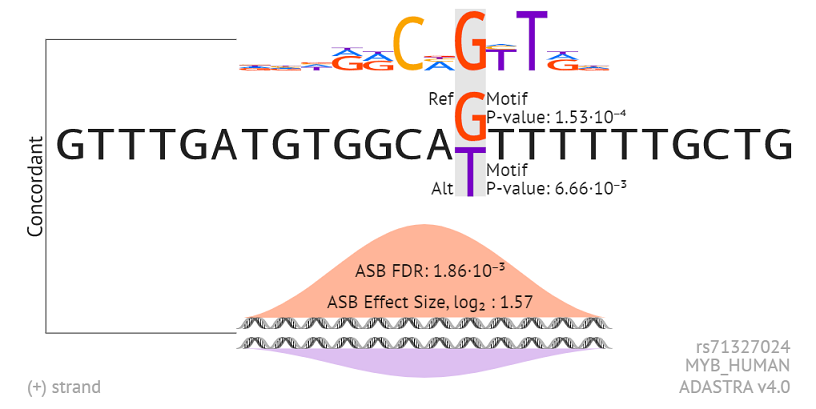
The alignment of the motif relative to the SNP is shown at the top. Motif P-values indicate the predicted binding specificities for the alternative alleles. The preferred allele according to ADASTRA data along with the ASB FDR and Effect Size is shown at the bottom. The higher bell corresponds to the allele preferentially bound by the TF in vivo according to the underlying ChIP-Seq data. The DNA strand/orientation is marked in the bottom left corner.
Software
- API
- For programmatic access, ADASTRA API is available at https://adastra.autosome.org/api/
- BABACHI
- BABACHI is available on GitHub
- ADASTRA pipeline
- ADASTRA pipeline is available on GitHub
External resources
Resources and databases used to annotate ADASTRA ASBs
- dbSNP build 151
- GENCODE v35
- HOCOMOCO v11
- GTEx release V8
- ClinVar release 9/05/2019
- NHGRI-EBI GWAS release 8/27/2019 with EFO mappings
- PheWAS catalog release V8
- GRASP build 2.0.0.0
- BROAD fine-mapping
Browser compatibility
Browser compatibility was checked using Sauce Labs and BrowserStack.
| OS | Version | Chrome | Firefox | Microsoft Edge | Opera | Safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linux | Ubuntu 18.04 | 93 | 92 | n/a | not tested | n/a |
| MacOS | Catalina, Mojave | 93 | 92 | n/a | 79 | 11.1 |
| Windows | 10 | 93 | 92 | 93 | 79 | n/a |